How to recognize symptoms
- Stop breathing regularly while sleeping and snoring loudly
- Having a sore throat, a dry mouth or headaches when waking up
- Failing to stay asleep or having insomnia
- Feeling sleepy during the day or having a tendency to fall asleep suddenly, being out of breath when waking up
- Suffering from libido or erection problems
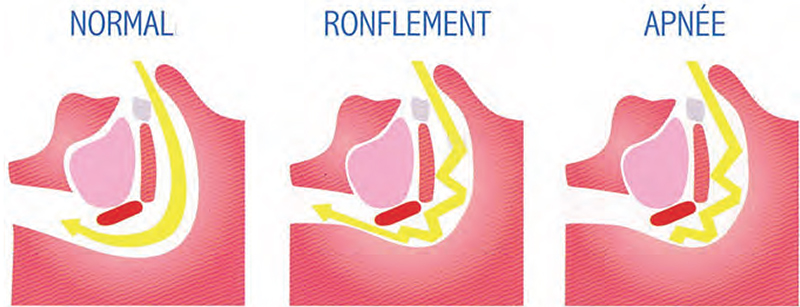
Sleep apnea syndrome mechanisms?
This is a succession of involuntary breathing stops that causes a decrease in oxygen supply during sleep. These breathing pauses are caused by loosening of the pharyngeal muscles and blockage of the trachea. The repetition of low oxygen levels causes cerebral arousals and a significant increase in heart rate.
Consequences of an untreated sleep apnea syndrome
- Hypertension: Each sudden micro-wakeup causes an increase in blood pressure and heart rate.
- Stroke: Each sudden awakening is accompanied by a dose of epinephrine that increases blood clotting and therefore the risk of stroke.
- Heart rhythm disorder: In the long term, sleep apnea is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular problems.
- Myocardial infarction: In severe apnea, the risk of sudden death during sleep is increased.
- Road accidents: Fatigue, daytime sleepiness and a reduced level of attention increase the risk of falling asleep while driving.
What are the factors that increase the risks of sleep apnea syndrome?
- Nasal congestion: People who often have a stuffy nose are more prone to sleep apnea.
- Alcohol: consumption leads to relaxation of the throat muscles which increases the frequency and duration of sleep apnea.
- Tranquilizers or sleeping pills: aggravate apnea for the same reasons as alcohol.
- Smoking: As it causes inflammation of the airways, it increases the risk of sleep apnea.
- Thick neck: the wider the neck, the higher the risk of sleep apnea.
- Heredity: In some families, sleep apnea syndrome is very common due to genetic susceptibility.
- Weight gain and obesity: one of the most visible consequences of untreated sleep apnea.
- Cardiovascular Disease or Stroke: People with hypertension and heart failure are often apneic.


